Fancy JS terms & Node
Leon Noel

#100Devs
"I can't go to Outback, I got too much at stake"
Agenda
- Questions?
- Let's Talk - #100Devs
- Learn - JS All Lies
- Learn - Call Stack / Task Queue
- Learn - Event Loop
- Learn - Node
- Homework - Coin Flip & RPS
Questions
About last class or life

Checking In

Like and Retweet the Tweet
!checkin
Office Hours

SUNDAY
1:00pm EST
Networking

Alternatives?
1 coffee chat this week
USE THE SHEET!

NOW WITH TWO TABS!: Google Sheet
Grab The Checklist
!checklist
PUSH EVERY DAY

Submitting Work

Submitting Work

Spaced Repetition
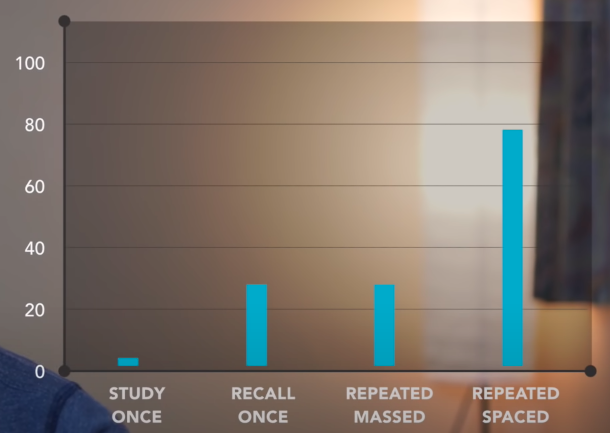
Ali Abdaal: https://youtu.be/Z-zNHHpXoMM
Thank You
Philip Roberts
Jake Archibald
Watch These Videos (Homework)
Backend!

Butt first!
Javascript is
single-threaded
Synchronous aka processes
one operation at a time

vs



If synchronous, how do we do stuff like make an api request and keep scrolling or clicking
Things should block
THE ENVIRONMENT

Not This

THIS
Our JS is running in
a browser
Browsers have a BUNCH of APIs we can use that are async and enable us to keeping looking a cute cat photos while those operations are being processed asynchronously
Common browser APIs

DOM (Document Object Model) API
WAIT
WHAT THE FUCK
WHAT THE FUCK
Actual words Leon said when figuring all this shit out...

So, yeah, JS can do a lot of "blocking" stuff in the browser because it is handing that stuff off to async
Web APIs
BUT
We are going to need to know how to handle responses coming back from those Web APIs
JS does this with callbacks, promises,
and eventually async/await
The Old School Way
Callbacks
You can have a function that takes another function as an argument
aka Higher Order Function

You have seen this a million times
addEventListener('click', callback)
A Callback is the function that has been passed as an argument
Callbacks are not really "a thing" in JS
just a convention
Callback fires when async task or another function
is done
function houseOne(){
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
}, 3000)
}, 4000)
}, 5000)
}
houseOne()Welcome To Hell

Callback Hell
What if there was a more readable way to handle async code
Promise
An object that MAY have a value in
the future
.then()
A promise object method that runs after the promise "resolves"
.then(value)
Whatever value the promise object has gets passed as an argument
We've Seen This Before

APIs
Fetch Fido, Fetch!
fetch("https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random")
.then(res => res.json()) // parse response as JSON
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(`error ${err}`)
});
Fetch returns a Promise
Like a bunch of Web APIs running async code
function houseOne(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Paper delivered to house 1')
}, 1000)
})
}
function houseTwo(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Paper delivered to house 2')
}, 5000)
})
}
function houseThree(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Paper delivered to house 3')
}, 2000)
})
}
houseOne()
.then(data => console.log(data))
.then(houseTwo)
.then(data => console.log(data))
.then(houseThree)
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(err => console.log(err))Chaining Don't Read Good

I want my asynchronous code to look sychronous

Async / Await
A way to handle async responses
Promises Under The Hood

Syntactic sugar on top of promises, making asynchronous code easier to write and to read afterwards
Await waits for an async process to complete inside an Async Function
function houseOne(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Paper delivered to house 1')
}, 1000)
})
}
function houseTwo(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Paper delivered to house 2')
}, 5000)
})
}
function houseThree(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Paper delivered to house 3')
}, 2000)
})
}
async function getPaid(){
const houseOneWait = await houseOne()
const houseTwoWait = await houseTwo()
const houseThreeWait = await houseThree()
console.log(houseOneWait)
console.log(houseTwoWait)
console.log(houseThreeWait)
}
getPaid()async function getPaid(){
const houseOneWait = await houseOne()
const houseTwoWait = await houseTwo()
const houseThreeWait = await houseThree()
console.log(houseOneWait)
console.log(houseTwoWait)
console.log(houseThreeWait)
}
getPaid()
I Need Something Real

APIs
Fetch Fido, Fetch!
async function getACuteDogPhoto(){
const res = await fetch('https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random')
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
}
getACuteDogPhoto()
Let's Use A Web API
setTimeout()

setTimeout and setInterval are not part of the Javascript specification...
Most environments include them...
like all browsers and Node.js
function houseOne(){
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
}
function houseTwo(){
setTimeout(() => console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 3000)
}
function houseThree(){
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
}
houseOne()
houseTwo()
houseThree()function houseOne(){
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
}
function houseTwo(){
setTimeout(() => console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
function houseThree(){
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
}
houseOne()
houseTwo()
houseThree()EVENT LOOP

Time for some data structures
Queue

Like a real queue, the first element which was added to the list, will be the first element out.
This is called a FIFO (First In First Out) structure.

let queue = []
queue.push(2) // queue is now [2]
queue.push(5) // queue is now [2, 5]
let i = queue.shift() // queue is now [5]
alert(i) // displays 2Queue Example
Stack

The first pancake made, is the last pancake served.
This is called a stack.
The first element which was added to the list, will be the last one out. This is called a LIFO (Last In First Out) structure.
let stack = []
stack.push(2) // stack is now [2]
stack.push(5) // stack is now [2, 5]
let = stack.pop() // stack is now [2]
alert(i) // displays 5Stack Example
Back To Getting Got

JS IS RUNNING IN THE BROWSER
V8 Engine
(Parse Code > Runnable Commands)
Window Runtime (Hosting Environment)
Gives Us Access To Web APIs
Passes stuff to Libevent (Event Loop)
The Event Loop monitors the Callback Queue and Job Queue and decides what needs to be pushed to the Call Stack.
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
main()
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
main()
log('house 1')
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
main()
log('house 1')
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
main()
log('house 1')
setTimeout()
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
main()
log('house 1')
setTimeout()
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
main()
log('house 1')
setTimeout() - cb or promise...
log('house 3')
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
log('house 1')
setTimeout() - cb or promise...
log('house 3')
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
cb / promise
log('house 1')
log('house 3')
Call Stack
Web APIs
Task Queue
(Also, a job queue)
console.log('Paper delivered to house 1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Paper delivered to house 2'), 0)
}
console.log('Paper delivered to house 3')
Console
log('house 1')
log('house 3')
log('house 2')
Backend BABY

Does Javascript have access to the DOM natively (built in)?

Javascript needed Web APIs to handle async and a bunch of stuff in the Browser
JS is a language that can only do what the hosting environment allows
What Do Servers Need?
Disk Access
(hardrive/ssd)
&&
Network Access
(internet, request / responses)
What if there was a hosting environment that allowed JS to have disk and network access
Music & Light Warning - Next Slide
NODE.js BABY
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine.


The same shit that lets you run JS in the browser can now be used to run JS on Servers, Desktops, and elsewhere
True Story

V8 Engine Does All The Heavy Lifting
Engine Vs. Compiler
And just like the browser's Web APIs Node come with a bunch of stuff
Built in Modules
(libraries or collections of functions)
HTTP (network access)
FS (file system access)
Access to millions of packages via NPM
(groupings of one or more custom modules)
Not Web APIs, but C/C++ APIs
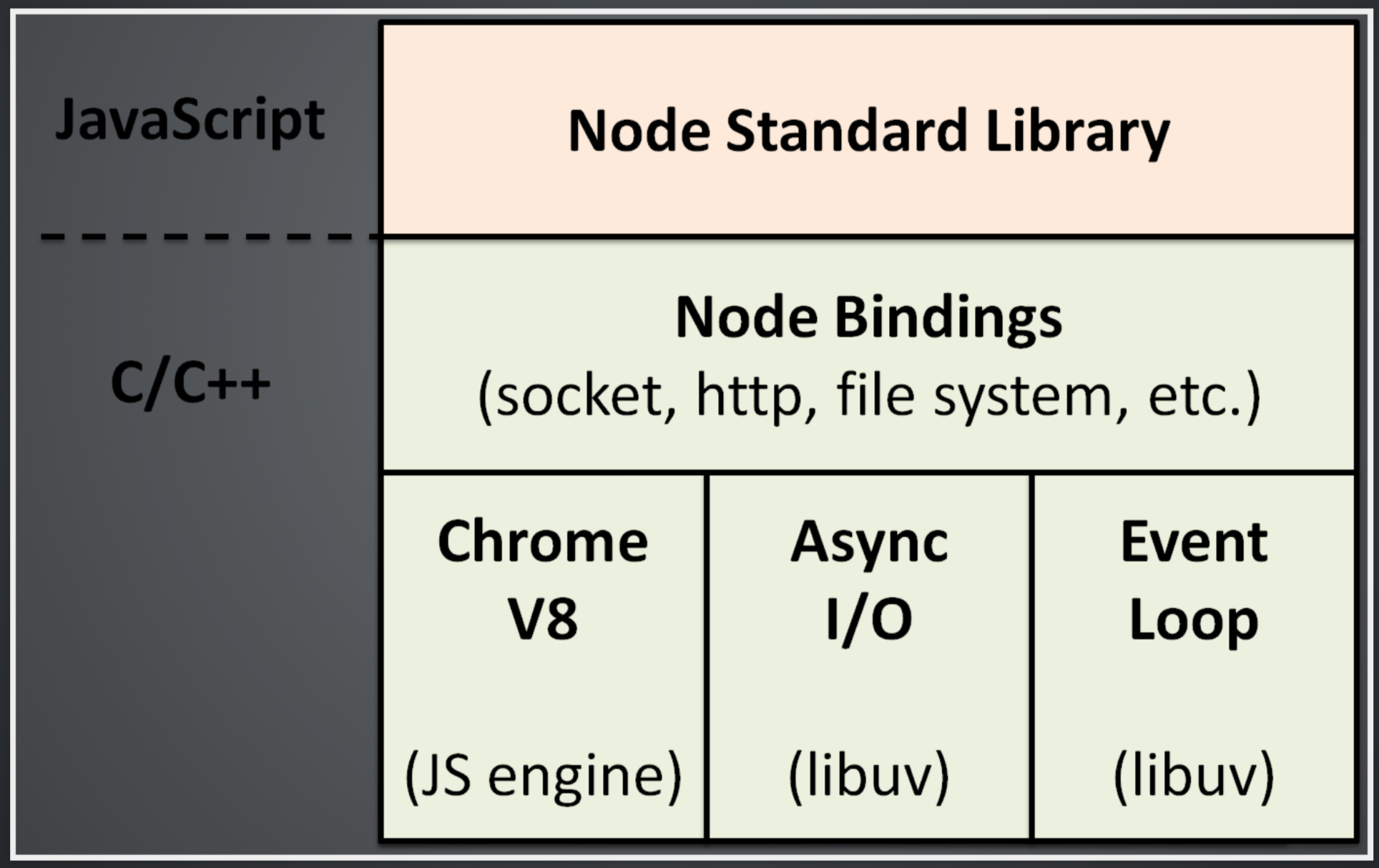
sorry, don't remember the source
Install Node
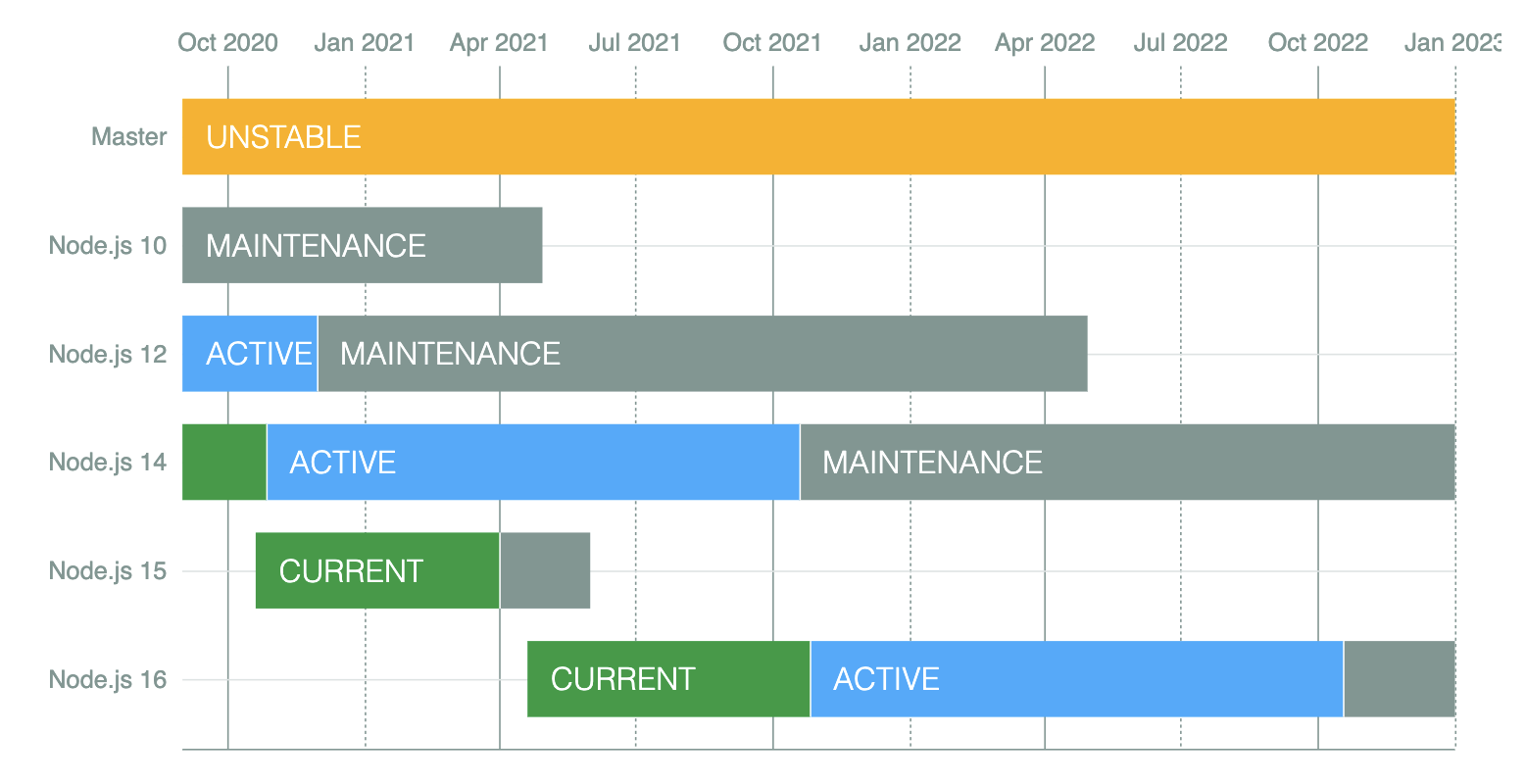
Releases?
LTS, Current, Nightly?
Let's Code
Simple Node Server

Just
HTTP & FS
const http = require('http')
const fs = require('fs')
http.createServer((req, res) => {
fs.readFile('demofile.html', (err, data) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'})
res.write(data)
res.end()
})
}).listen(8000)Music & Light Warning - Next Slide
You are now a
Software Engineer
that can build
Fullstack Web Applications

Let's Look
More Complex Backend


How could we clean this up?
Group Work

https://live.remo.co/e/100devs-networking-night-group-0
https://live.remo.co/e/100devs-networking-night-group-0-1
If Remo does not work for you, please jump into one of our
Discord Voice Channels!
Homework
Do: Start prepping THE BANK
Do: Complete Your Professional Links
Do: Make node-backend-simple-json more readable
Do: Make a coinflip game where the randomization happens server side
